Methylation status of Septin 9 in peripheral blood and its relationship with colorectal cancer
-
摘要:目的
检测结直肠癌(CRC)患者外周血胞裂蛋白9(Septin 9)的甲基化状态, 分析Septin 9甲基化与CRC的关系。
方法选取120例CRC患者为研究对象,分析其外周血Septin 9甲基化状态与临床资料的关系; 分离CRC患者和健康人群的血清外泌体,采用该外泌体处理CRC细胞,测定CRC细胞的增殖和凋亡情况。
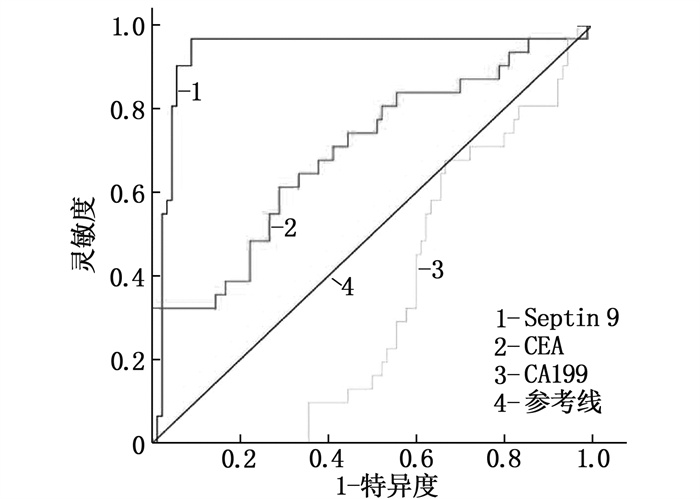
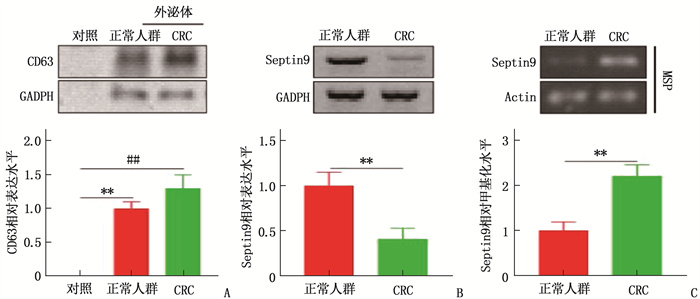
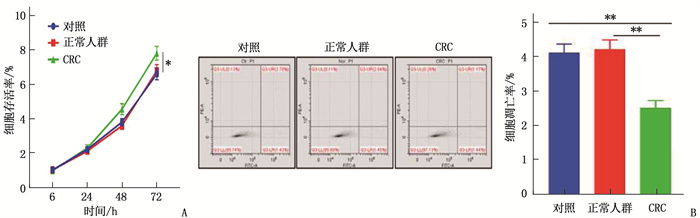
结果共计1586例体检人群接受了Septin 9筛查,其中Seprtin 9甲基化阳性56例,阳性率为3.5%。Sepetin 9阳性者中,胃肠状态异常者(肠胃炎症或者息肉)20例(35.7%), 而Septin 9阴性者胃肠状态异常率仅为5.4%(83/1530), 提示Septin 9在外周血中的甲基化状态与胃肠状态密切相关。120例CRC患者中, Septin 9甲基化阳性率为78.4%(73/93);在不同分化程度的比较中,高分化、中分化、低分化CRC患者的Septin 9甲基化阳性率依次为52.6%(10/19)、79.7%(59/74)、88.9%(24/27), 低分化CRC患者外周血Septin 9甲基化阳性率高于高分化组,差异有统计学意义(P=0.006)。外周血Septin 9甲基化的灵敏度为72.3%, 特异度为92.5%。Western blot结果显示CRC患者外泌体中Septin 9表达较健康人群降低,外泌体中Septin 9甲基化水平较正常人群上升,差异均有统计学意义(P=0.009、0.003)。本研究结果显示, CRC患者血清外泌体可促进细胞增殖,对细胞凋亡有抑制作用,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。
结论Septin 9可作为CRC早期筛查的标志物, CRC患者血清外泌体诱导的CRC增殖、凋亡抵抗可能是Septin 9的作用机制。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo detect the methylation status of Septin 9 in the peripheral blood of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) and analyze the relationship between the methylation of Septin 9 and CRC.
MethodsA total of 120 patients with CRC were selected as research objects, and the relationship between the methylation status of Septin 9 in the peripheral blood and the medical materials was analyzed; the serum exosomes isolated from patients with CRC and healthy people were used to treat the CRC cells, and the proliferation and apoptosis of CRC cells were detected.
ResultsA total of 1 586 people with health examinations were screened for Septin 9, and 56 of whom were positive for methylation of Septin 9, with a positive rate of 3.5%. Among patients with Septin 9 positive, there were 20 cases (35.7%) with abnormal gastrointestinal status (gastrointestinal inflammation or polyps), while only 5.4% (83/1 530) of patients with Septin 9 negative had abnormal gastrointestinal status, which indicated that the methylation status of Septin 9 in the peripheral blood was closely related to the gastrointestinal status. Among 120 CRC patients, the positive rate of methylation of Septin 9 was 78.4% (73/93); in the comparison of different differentiation degrees, the positive rates of Septin 9 methylation in patients with highly differentiated, moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated CRC were 52.6% (10/19), 79.7% (59/74) and 88.9% (24/27) respectively, and the positive rate of Septin 9 methylation in peripheral blood of patients with poorly differentiated CRC was significantly higher than that of patients with highly differentiated CRC (P=0.006). The sensitivity and specificity of Septin 9 methylation in the peripheral blood were 72.3% and 92.5% respectively. Western blot results showed that the expression of Septin 9 in the exosomes of CRC patients was significantly lower than that in the normal people, while the methylation level of Septin 9 in the exosomes was significantly higher than that in the healthy people (P=0.009, 0.003). The results of this study showed that serum exosomes of CRC patients could significantly promote cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01).
ConclusionSeptin 9 can be used as a marker for early screening of CRC, and the mechanism of Septin 9 may be the proliferation and apoptosis resistance of CRC induced by serum exosomes in patients with CRC.
-
Keywords:
- colorectal cancer /
- Septin 9 /
- exosomes /
- carcinoembryonic antigen /
- carbohydrate antigen 199 /
- diagnosis
-
-
表 1 1 586例正常人群Septin 9甲基化与胃肠状态的相关性
指标 分类 Septin 9甲基化状态 阳性(n=56) 阴性(n=1 530) 性别 男 43 982 女 13 548 胃肠状态 正常 36 1 447 异常 20 83 表 2 CRC患者Septin 9检测情况[n(%)]
指标 分类 Septin 9阳性(n=93) Septin 9阴性(n=27) 性别 男 67(79.8) 17(20.2) 女 26(72.2) 10(27.8) 年龄 ≤60岁 51(71.8) 20(28.2) >60岁 42(85.7) 7(14.3) 分化程度 高分化 10(52.6)** 9(47.4) 中分化 59(79.7) 15(20.3) 低分化 24(88.9) 3(11.1) 低分化比较, ** P < 0.01。 表 3 CRC患者Septin 9、CEA、CA199的灵敏度和特异度比较
指标 灵敏度(95%CI) 特异度(95%CI) 曲线下面积 Septin 9 72.3(60.5~80.5) 92.5(75.5~95.5) 0.87 CEA 42.2(32.2~55.6) 75.0(65.5~87.5) 0.59 CA199 20.5(12.1~27.1) 45.0(37.7~55.5) 0.24 -
[1] ZENG H M, ZHENG R S, GUO Y M, et al. Cancer survival in China, 2003-2005: a population-based study[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015, 136(8): 1921-1930. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29227
[2] KANG Q, JIN P, YANG L, et al. Significance of Septin 9 gene methylation detection of plasma circulation DNA in colorectal cancer screening[J]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2014, 94(48): 3839-3841. .
[3] SUN G P, MENG J, DUAN H, et al. Diagnostic ssessment of Septin 9 DNA methylation for colorectal cancer using blood detection: a meta-analysis[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2019, 25(4): 1525-1534. doi: 10.1007/s12253-018-0559-5
[4] LIU T, ZHANG X, DU L T, et al. Exosome transmitted miR-l 28-3p increase chemosensitivity of oxaliplatin-resistant coloretal cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 43. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-0981-7
[5] 谭琪, 宗明, 處珊珊, 等. 联合检测外周血游离Septin 9、SDC2、BCATI基因甲基化在结直肠癌诊断中的意义[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2021, 44(3): 204-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMXZ201605028.htm [6] YANQING H, CHENG D, LING X. Serum CA72-4 as a bionarker in the diagnosis of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. Open Med: Wars, 2018, 13: 164-171. doi: 10.1515/med-2018-0026
[7] 宋慧琴, 张君娜. Septin 9基因、缺氧诱导因子1与结直肠癌发生发展的相关性[J]. 广州医科大学学报, 2021, 49(1): 14-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-9664.2021.01.04 [8] YANG J K, YANG J P, TONG J, et al. Exosomal miR-221 targets DNM3 to induce tumor progression and temozolomide re sistance in glioma[J]. J Neurooncol, 2017, 131(2): 255-265. doi: 10.1007/s11060-016-2308-5
[9] 陈培, 邓钦木, 李丹丹. 血浆Septin 9甲基化检测在结直肠癌中的诊断价值[J]. 现代检验医学杂志, 2020, 35(4): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7414.2020.04.003 [10] 宫媛, 王卫华, 杜海涛, 等. 外周血Septin 9基因甲基化检测在结直肠癌诊断中的研究进展[J]. 临床输血与检验, 2021, 23(2): 263-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2587.2021.02.028 [11] 张春燕, 于正麟, 王蓓丽, 等. 血浆Septin 9基因甲基化检测性能评价及对结直肠癌患者的筛查价值[J]. 临床检验杂志, 2019, 37(2): 152-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCJY201902018.htm [12] YAN S S, HAN B, GAO S Y, et al. Exsome-encapsulated micro RNAs as circulating biomarkers for colorectal cancer[J] Oncotarget, 2017, 8(36): 60149-60158. . doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18557
[13] 陈越亚, 陈卫昌. 外周血SEPT9基因甲基化检测在结直肠癌中的研究进展[J]. 中国血液流变学杂志, 2021, 31(2): 265-270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-881X.2021.02.031 [14] 穆剑强, 高海锋. 外周血Septin9基因甲基化和血清CA199联合检测在结直肠癌筛查中的诊断价值[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2022, 19(4): 526-529. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYYL202204023.htm [15] RICHARDS K E, ZELENIAK A E, FISHEL M L, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast exosomes regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36(13): 1770-1778.
[16] 赵媛, 陈四明, 蒋益兰, 等. Septin-9基因甲基化检测对结直肠癌诊断价值的meta分析[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2020, 22(6): 852-856. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn431274-20200222-00172 -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 黄艳,梁玉美,冯燕妮,杨松媚. 外周血受体相互作用蛋白激酶3、混合系列蛋白激酶样结构域水平与新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎病情严重程度的关系. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(01): 62-67 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 庄丽霞,张结,陈培鑫. 血清转化生长因子-β1、肠碱性磷酸酶诊断重症新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的应用价值研究. 实用临床医药杂志. 2023(19): 67-70 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 梁元豪,郭红梅,梁燕勇,王霞. 超声和X线片检查运用于新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的诊断效果观察. 中外医学研究. 2021(05): 78-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 温晓敏,张爱明,叶明阳,王文翔. 尿I-FABP联合CBG诊断新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的价值分析. 中国实验诊断学. 2021(06): 853-857 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张宁,杨秀玲. X线评分量表联合腹部超声可较好识别新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎:89例前瞻性研究. 分子影像学杂志. 2021(03): 526-530 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 苏嘉鸿,钟陈,胡小华. 新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎和先天性巨结肠肠穿孔的鉴别诊断和治疗分析. 世界复合医学. 2021(10): 115-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 余凤,蒋双兰,毛伟豪. 新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的早期诊断及效果观察. 现代医用影像学. 2020(01): 137-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 黄文生,钟小明,罗开源,肖洪亮,郭荣华,黄毅,谢海燕. 钙卫蛋白结合直肠液渗透压在NEC诊断及病情监测中的应用研究. 中国现代医生. 2020(19): 14-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王晶,曾朝强,张福洲,陈世孝,母其文,尚彪,田鹏. 新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的X线诊断分析. 实用医学影像杂志. 2020(05): 456-458 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 范文婷,廖伟. 新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎发生的主要危险因素及手术时机对预后影响的回顾性分析. 川北医学院学报. 2019(06): 679-682 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
