Long non-coding RNA MIR22HG regulates CTLA4 through microRNA-9-3p to inhibit prostate cancer
-
摘要:目的
探讨长链非编码RNA(LncRNA)MIR22HG通过微小RNA-9-3p(miR-9-3p)调节细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关蛋白4(CTLA4)抑制前列腺癌的机制。
方法收集26例前列腺癌组织样本和26例前列腺增生组织样本,培养VCAP、PC3、LNCap和DU145细胞。采用实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)检测前列腺癌组织、前列腺增生组织及4种前列腺癌细胞的MIR22HG和miR-9-3p mRNA水平。筛选MIR22HG和miR-9-3p mRNA表达较高的细胞。将筛选出的细胞按不同干预方法分为OE-CTLA4(CTLA4过表达组)、OE-MIR22HG(MIR22HG过表达组)、miR-9-3p mimic(miR-9-3p过表达组)、OE-MIR22HG+miR-9-3p mimic(MIR22HG及miR-9-3p联合过表达组)、OE-NC+NC mimic(转染对照组)、NC mimic(miR-9-3p过表达对照组)。采用TargetScan数据库及荧光素酶报告基因实验验证MIR22HG与miR-9-3p及miR-9-3p与CTLA4是否存在靶向抑制关系。采用qRT-PCR及Western blot检测各组细胞MIR22HG和miR-9-3p mRNA及CTLA4蛋白表达。取裸鼠96只,按干预方法不同分为OE-NC+NC mimic组(转染对照)、OE-MIR22HG组(MIR22HG过表达)及OE-MIR22HG+miR-9-3p mimic组(MIR22HG及miR-9-3p联合过表达),每组32只。接种后4周期间,每周检测小鼠原位移植瘤并统计瘤体的质量和体积变化。
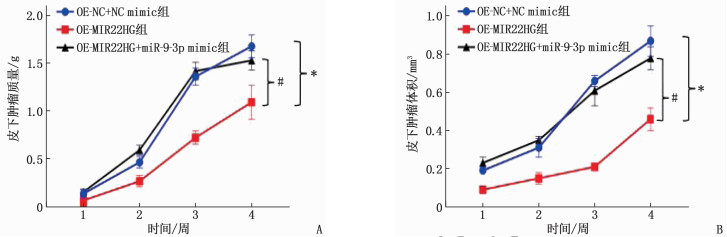
结果前列腺癌细胞VCAP、PC3、LNCap和DU145细胞中, PC3细胞MIR22HG mRNA相对较低, miR-9-3p mRNA相对较高,因此选择PC3细胞进行研究。在PC3细胞中成功过表达MIR22HG, 荧光素酶报告基因实验验证了MIR22HG和miR-9-3p的靶向抑制关系,过表达MIR22HG, miR-9-3p表达下调,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。TargetScan数据库预测免疫基因CTLA4和miR-9-3p的靶向关系,荧光素酶报告基因实验验证miR-9-3p和CTLA4的靶向抑制关系,过表达miR-9-3p, CTLA4表达上调,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。过表达MIR22HG的裸鼠皮下肿瘤的质量降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。OE-MIR22HG+miR-9-3p mimic组裸鼠皮下肿瘤的质量、体积与OE-NC+NC mimic组比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
结论MIR22HG与miR-9-3p存在靶向负调节关系, miR-9-3p与CTLA-4存在靶向调节关系, MIR22HG/miR-9-3p可能通过抑制CTLA4达到免疫治疗前列腺癌的目的。
-
关键词:
- 长链非编码RNA MIR22HG /
- 微小RNA-9-3p /
- 细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关蛋白4 /
- 前列腺癌
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the mechanism of long-chain non-coding RNA (LncRNA) MIR22HG to regulate cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4 (CTLA4) through microRNA-9-3p (miR-9-3p) to inhibit prostate cancer.
MethodsVCAP, PC3, LNCap and DU145 cells were cultured from Samples of 26 patients with prostate cancer and 26 patients with prostatic hyperplasia. MIR22HG and miR-9-3p mRNA levels in prostate cancer tissue, prostate hyperplasia tissue and 4 types of prostate cancer cells were determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The cells with higher expression of MIR22HG and miR-9-3p mRNA were screened. The selected cells were divided into OE-CTLA4 (CTLA4 overexpression group), OE-MIR22HG (MIR22HG overexpression group), miR-9-3p mimic (miR-9-3p overexpression group), OE-MIR22HG+miR-9-3p mimic (MIR22HG and miR-9-3p co-overexpression group), OE-NC+NC mimic (transfection control group) and NC mimic (miR-9-3p overexpression control group). TargetScan database and luciferase reporter gene experiments were used to verify whether MIR22HG and miR-9-3p and miR-9-3p and CTLA4 had targeted inhibition relationships. The mRNA expression of MIR22HG and miR-9-3p and the protein expression of CTLA4 were detected by qRT-PCR and Western blot. A total of 96 nude mice were taken, and they were divided into OE-NC+NC mimic group (transfection control), OE-MIR22HG group (MIR22HG overexpression) and OE-MIR22HG+miR-9-3p mimic group (MIR22HG and miR-9-3p co-overexpression) according to the intervention methods, with 32 mice in each group. The tumors were transplanted in situ and the changes in body mass and volume of the tumors were measured each week for 4 weeks after inoculation.
ResultsAmong adenocarcinoma cells VCAP, PC3, LNCap and DU145 cells, PC3 cells showed a relatively low MIR22HG mRNA and a relatively high miR-9-3p mRNA, so PC3 cells were selected for the study. The MIR22HG in PC3 cells was successful overexpressed, luciferase reporter gene assay verified the targeted inhibition relationship between MIR22HG and miR-9-3p, and the expression of miR-9-3p in the overexpression of MIR22HG was significantly down-regulated (P < 0.05). TargetScan database predicted the targeting relationship between immune gene CTLA4 and miR-9-3p, luciferase reporter gene assay verified the targeted inhibition relationship between miR-9-3p and CTLA4, and the expression of CTLA4 overexpressing miR-9-3p was significantly up-regulated (P < 0.05). The weight of subcutaneous tumor in nude mice overexpressed MIR22HG was significantly decreased (P < 0.05). The weight and volume of subcutaneous tumors after OE-MIR22HG+miR-9-3p mimic group showed no significant differen compared with those of the OE-NC+NC mimic group (P>0.05).
ConclusionThere is a negative regulatory relationship between MIR22HG and miR-9-3p, and there is a negative regulatory relationship between miR-9-3p and CTLA4. MIR22HG/miR-9-3p may achieve the purpose of immunotherapy for prostate cancer by inhibiting CTLA4.
-
-
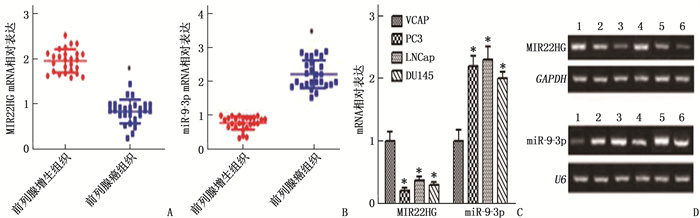
图 1 前列腺癌组织及细胞的MIR22HG和miR-9-3p mRNA相对表达
A: qRT-PCR检测前列腺癌组织中MIR22HG的表达(与前列腺增生组织比较, *P < 0.05); B: qRT-PCR检测前列腺癌组织中miR-9-3p的表达(与前列腺增生组织比较, *P < 0.05); C: qRT-PCR检测前列腺癌细胞中MIR22HG和miR-9-3p的表达(与VCAP相比, *P < 0.05); D: qRT-PCR检测前列腺癌组织、前列腺癌细胞中MIR22HG和miR-9-3p的表达(1: 前列腺癌组织; 2: 正常前列腺增生组织; 3: VCAP; 4: PC3; 5: LNCap; 6: DU145)。
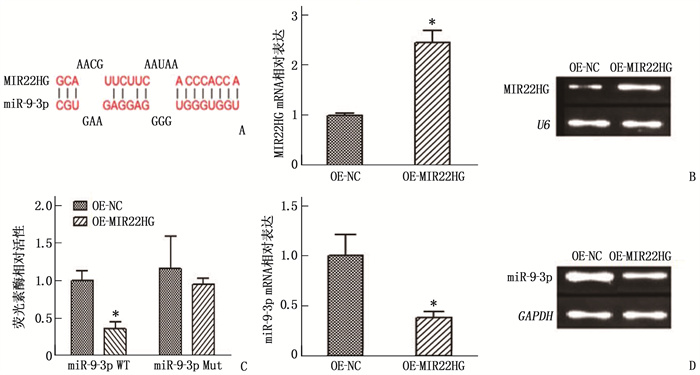
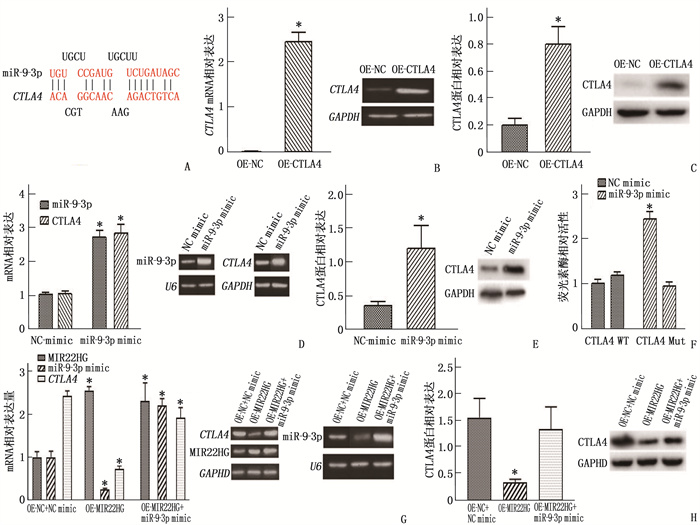
图 3 MIR22HG通过抑制miR-9-3p调控免疫基因CTLA4
A: miR-9-3p和CTLA4的靶向作用位点; B: qRT-PCR检测过表达CTLA4后, CTLA4 mRNA表达(与OE-NC比较, *P < 0.05); C: Western blot检测过表达CTLA4后, CTLA4蛋白表达(与OE-NC比较, *P < 0.05); D: qRT-PCR检测过表达miR-9-3p后, CTLA4 mRNA表达(与NC mimic比较, *P < 0.05); E: Western blot检测过表达miR-9-3p后, CTLA4蛋白表达(与NC mimic比较, *P < 0.05); F: 荧光素酶报告实验检测miR-9-3p和CTLA4的靶向作用(与NC mimic比较, *P < 0.05); G: qRT-PCR检测过表达MIR22HG和miR-9-3p后, CTLA4的表达情况(与OE-NC+NC mimic比较, *P<0.05); H: Western blot检测过表达MIR22HG和miR-9-3p后, CTLA4的表达情况(与OE-NC+NC mimic比较, *P<0.05)。
-
[1] MIYAHIRA A K, SHARP A, ELLS L, et al. Prostaitle eaner research: the mext generation; report from the 2019 CoffeyHoden Prustate Cancer Academy Meeting[J]. Prostate, 2020, 80(2): 113132.
[2] RAITINEN P, NEMIST0 K, PENNANEN E, et al. Circulatory and prostaie isse lpionie profles shifs afler high-dose alorvasatin use in men with prostate cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 12016. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68868-5
[3] ZHANG G X, LAN Y J, XIE A M, et al. Comprebensive analysis of long noncoding RNA (IneRNA)-chromatin intenctions reveals IneRNA functions dependent on binding diverse regulatony elements[J]. J Biol Chem, 2019, 294(43): 15613-15622. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008732
[4] LONG H, LI Q, XIAOZ P, et al. LneRNA MIR22HG promoles asteoarthritis progression ria regulating miR-9-3pVADAMTSS pathway[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(1): 3148-3158. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1945362
[5] ZHANG L, LI C X, SU X L. FEnenging impadt of the long noncoding RNA MIR22HG on polifenation and apoposis in muliple hummn cancers[J]. J Exp Cin Cancer Res, 2020, 39(1): 271. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01784-8
[6] HAVEL J J, CHOWELL D, CHAN T A. The evolving landscape of biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2019, 19(3): 133-150. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0116-x
[7] KRUGER S, ILMER M, KOBOLD S, et al. Advances in cancer immunotherapy 2019-latest trends[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 268. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1266-0
[8] TEWARI A K, STOCKERT J A, YADAV S S, et al. Inflammation and prostate cancer[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2018, 1095: 41-65.
[9] SFANOS K S, DE MARZO A M. Prostate cancer and inflammation: the evidence[J]. Histopathology, 2012, 60(1): 199-215. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.04033.x
[10] GUREL B, LUCIA M S, THOMPSON I M Jr, et al. Chronic inflammation in benign prostate tissue is associated with high-grade prostate cancer in the placebo arm of the prostate cancer prevention trial[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2014, 23(5): 847-856. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-1126
[11] SFANOS K S, ISAACS W B, DE MARZO A M. Infections and inflammation in prostate cancer[J]. Am J Clin Exp Urol, 2013, 1(1): 3-11.
[12] XU J, SHAO T T, SONG M X, et al. MIR22HG acts as a tumor suppressor via TGFβ/SMAD signaling and facilitates immunotherapy in colorectal cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 51. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01174-w
[13] 王蓉, 钱崇崴, 田亦文, 等. 微小RNA-9-3p对甲状腺乳头状癌细胞侵袭迁移和Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2018, 23(12): 1063-1068. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2018.12.002 [14] CHEN H, ALI M, RUBEN A, et al. E2F6-mediated downregulation of MIR22HG facilitates the progression of laryngocarcinoma by targeting the miR-5000-3p/FBXW7 axis[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 40(10): e00496-e00419.
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 黄艳,梁玉美,冯燕妮,杨松媚. 外周血受体相互作用蛋白激酶3、混合系列蛋白激酶样结构域水平与新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎病情严重程度的关系. 实用临床医药杂志. 2024(01): 62-67 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 庄丽霞,张结,陈培鑫. 血清转化生长因子-β1、肠碱性磷酸酶诊断重症新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的应用价值研究. 实用临床医药杂志. 2023(19): 67-70 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 梁元豪,郭红梅,梁燕勇,王霞. 超声和X线片检查运用于新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的诊断效果观察. 中外医学研究. 2021(05): 78-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 温晓敏,张爱明,叶明阳,王文翔. 尿I-FABP联合CBG诊断新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的价值分析. 中国实验诊断学. 2021(06): 853-857 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张宁,杨秀玲. X线评分量表联合腹部超声可较好识别新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎:89例前瞻性研究. 分子影像学杂志. 2021(03): 526-530 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 苏嘉鸿,钟陈,胡小华. 新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎和先天性巨结肠肠穿孔的鉴别诊断和治疗分析. 世界复合医学. 2021(10): 115-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 余凤,蒋双兰,毛伟豪. 新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的早期诊断及效果观察. 现代医用影像学. 2020(01): 137-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 黄文生,钟小明,罗开源,肖洪亮,郭荣华,黄毅,谢海燕. 钙卫蛋白结合直肠液渗透压在NEC诊断及病情监测中的应用研究. 中国现代医生. 2020(19): 14-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王晶,曾朝强,张福洲,陈世孝,母其文,尚彪,田鹏. 新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的X线诊断分析. 实用医学影像杂志. 2020(05): 456-458 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 范文婷,廖伟. 新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎发生的主要危险因素及手术时机对预后影响的回顾性分析. 川北医学院学报. 2019(06): 679-682 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备 32100302010246号
苏公网安备 32100302010246号
